给寻找编程代码教程的朋友们精选了相关的编程文章,网友糜月灵根据主题投稿了本篇教程内容,涉及到MybatisPlus、BaseMapper、数据库增删改查、MybatisPlus增删改查、MybatisPlus BaseMapper 数据库增删改查相关内容,已被475网友关注,如果对知识点想更进一步了解可以在下方电子资料中获取。
MybatisPlus BaseMapper 数据库增删改查
MybatisPlus 是一款在 Mybatis 基础上进行的增强 orm 框架,可以实现不写 sql 就完成数据库相关的操作。普通的 mapper 接口通过继承 BaseMapper 接口,即可获得增强,如下所示:
public interface UserMapper extends BaseMapper<User> {
}接下来就对其源码一探究竟,看看他到底是如何实现的
环境搭建
1、使用 h2 数据库,方便测试,导入相关依赖
dependencies {
implementation 'org.springframework.boot:spring-boot-starter-web:2.7.1'
implementation 'com.baomidou:mybatis-plus-boot-starter:3.5.3.1'
implementation 'org.projectlombok:lombok:1.18.24'
implementation 'com.h2database:h2:1.4.200'
}2、springboot 配置文件
spring:
datasource:
driver-class-name: org.h2.Driver
username: root
password: test
sql:
init:
schema-locations: classpath:db/schema-h2.sql
data-locations: classpath:db/data-h2.sql3、resources 目录下新建 db 目录,创建 sql 文件
schema-h2.sql
DROP TABLE IF EXISTS demo_user;
CREATE TABLE demo_user
(
id int primary key,
name varchar,
age int,
email varchar
);data-h2.sql
DELETE
FROM demo_user;
INSERT INTO demo_user (id, name, age, email)
VALUES (1, 'Jone', 18, 'test1@baomidou.com'),
(2, 'Jack', 20, 'test2@baomidou.com'),
(3, 'Tom', 28, 'test3@baomidou.com'),
(4, 'Sandy', 21, 'test4@baomidou.com'),
(5, 'Billie', 24, 'test5@baomidou.com');4、编写 mapper 文件
public interface UserMapper extends BaseMapper<User> {
}5、启动测试
@MapperScan("org.example.mapper")
@SpringBootApplication
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ConfigurableApplicationContext context = SpringApplication.run(Main.class, args);
UserMapper userMapper = context.getBean(UserMapper.class);
System.out.println(userMapper.selectList(null));
}
}结果如下
[User(id=1, name=Jone, age=18, email=test1@baomidou.com), User(id=2, name=Jack, age=20, email=test2@baomidou.com), User(id=3, name=Tom, age=28, email=test3@baomidou.com), User(id=4, name=Sandy, age=21, email=test4@baomidou.com), User(id=5, name=Billie, age=24, email=test5@baomidou.com)]
从 @MapperScan 入手
@MapperScan 注解的作用是扫描指定 mapper 接口所在的包,并生成接口的代理对象,注入到 ioc 容器中,接口定义如下
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Target(ElementType.TYPE)
@Documented
@Import(MapperScannerRegistrar.class)
@Repeatable(MapperScans.class)
public @interface MapperScan {
}可以看到 Import 了个 MapperScannerRegistrar,点进去看看这个类做了什么
@Override
public void registerBeanDefinitions(AnnotationMetadata importingClassMetadata, BeanDefinitionRegistry registry) {
AnnotationAttributes mapperScanAttrs = AnnotationAttributes
.fromMap(importingClassMetadata.getAnnotationAttributes(MapperScan.class.getName()));
if (mapperScanAttrs != null) {
// 注册一个 beanDefinition
registerBeanDefinitions(importingClassMetadata, mapperScanAttrs, registry,
generateBaseBeanName(importingClassMetadata, 0));
}
}
void registerBeanDefinitions(AnnotationMetadata annoMeta, AnnotationAttributes annoAttrs,
BeanDefinitionRegistry registry, String beanName) {
// 注册MapperScannerConfigurer的BeanDefinition
BeanDefinitionBuilder builder = BeanDefinitionBuilder.genericBeanDefinition(MapperScannerConfigurer.class);
// ......
registry.registerBeanDefinition(beanName, builder.getBeanDefinition());
}这个 importRegister 注册了一个 MapperScannerConfigurer,这个类是个 BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor,核心逻辑就是在这个类中,即扫描指定 mapper 接口所在的包,并生成接口的代理对象,注入到 ioc 容器中,查看该类的 postProcessBeanDefinitionRegistry() 方法
@Override
public void postProcessBeanDefinitionRegistry(BeanDefinitionRegistry registry) {
if (this.processPropertyPlaceHolders) {
processPropertyPlaceHolders();
}
ClassPathMapperScanner scanner = new ClassPathMapperScanner(registry);
// 设置一些scanner参数
scanner.setSqlSessionTemplate(this.sqlSessionTemplate);
// ......
// 扫描mapper接口
scanner.scan(
StringUtils.tokenizeToStringArray(this.basePackage, ConfigurableApplicationContext.CONFIG_LOCATION_DELIMITERS));
}进入父类 scan 方法,发现核心方法是子类的 doScan(), 来到 MapperScannerConfigurer.doScan()
@Override
public Set<BeanDefinitionHolder> doScan(String... basePackages) {
// 拿到扫描到的 beanDefinition
Set<BeanDefinitionHolder> beanDefinitions = super.doScan(basePackages);
if (beanDefinitions.isEmpty()) {
LOGGER.warn(() -> "No MyBatis mapper was found in '" + Arrays.toString(basePackages)
+ "' package. Please check your configuration.");
} else {
// 处理 mapper beanDefinition
processBeanDefinitions(beanDefinitions);
}
return beanDefinitions;
}核心在 processBeanDefinitions(beanDefinitions) 中
private void processBeanDefinitions(Set<BeanDefinitionHolder> beanDefinitions) {
AbstractBeanDefinition definition;
BeanDefinitionRegistry registry = getRegistry();
for (BeanDefinitionHolder holder : beanDefinitions) {
definition = (AbstractBeanDefinition) holder.getBeanDefinition();
// 设置该BeanDefinition的beanClass是 MapperFactoryBean
definition.setBeanClass(this.mapperFactoryBeanClass);
// ......
// 设置该MapperFactoryBean 中的 sqlSessionTemplateBeanName
if (StringUtils.hasText(this.sqlSessionTemplateBeanName)) {
definition.getPropertyValues().add("sqlSessionTemplate",
new RuntimeBeanReference(this.sqlSessionTemplateBeanName));
explicitFactoryUsed = true;
}
// ......
}
}通过这一系列源码,可以知道,@MapperScan 指定的包在 MapperScannerConfigurer 被扫描成 BeanDefinition, 并且修改了 BeanDefinition 的 beanClass 属性为 MapperFactory,这样 spring 实例化 UserMapper 单例 bean 时,会生成对应的 MapperFactory
看看这个 MapperFactory 是什么鬼
public class MapperFactoryBean<T> extends SqlSessionDaoSupport implements FactoryBean<T> {
@Override
public T getObject() throws Exception {
return getSqlSession().getMapper(this.mapperInterface);
}
public SqlSession getSqlSession() {
return this.sqlSessionTemplate;
}
}这个类是个 FactoryBean,那么它的 getObject() 方法就是调用 sqlSessionTemplate 的 getMapper() 方法获取代理对象,关于这个 getMapper() 方法的解析,可以参考我之前写的《Mybatis 通过接口实现 sql 执行原理解析》
到这里,MapperFactory 生成的 bean 被放到了 ioc 容器中,结束了吗?我们忽略了 MapperFactory 的父类 SqlSessionDaoSupport,下面一节来看看这个父类 SqlSessionDaoSupport 做了什么
SqlSessionDaoSupport
这个类看名字是给 Dao 做支持的,Dao 指的就是那个 mapper 接口,做什么支持?其实给就是给 BaseMapper 里定义的方法生成对应的 Statemnet,注册到 MybatisMapperRegistry 中,这样调用 BaseMapper 方法时,代理类就会从 MybatisMapperRegistry 中找到 Statemnet,这样可以取出 sql 执行了,来看源码,其他都是抽象方法,只有一个初始化方法
@Override
public final void afterPropertiesSet() throws IllegalArgumentException, BeanInitializationException {
// 让子类处理
checkDaoConfig();
// Let concrete implementations initialize themselves.
try {
initDao();
}
catch (Exception ex) {
throw new BeanInitializationException("Initialization of DAO failed", ex);
}
}调用了抽象方法,子类实现了 checkDaoConfig(),来看下 MapperFactoryBean.checkDaoConfig()
protected void checkDaoConfig() {
super.checkDaoConfig();
Assert.notNull(this.mapperInterface, "Property 'mapperInterface' is required");
Configuration configuration = this.getSqlSession().getConfiguration();
if (this.addToConfig && !configuration.hasMapper(this.mapperInterface)) {
try {
// 解析这个 mapper 方法
configuration.addMapper(this.mapperInterface);
} catch (Exception var6) {
this.logger.error("Error while adding the mapper '" + this.mapperInterface + "' to configuration.", var6);
throw new IllegalArgumentException(var6);
} finally {
ErrorContext.instance().reset();
}
}
}看到 configuration.addMapper(this.mapperInterface) 方法,相信看过 mybatis 源码的小伙伴们已经知道要干什么了吧。就是解析这个 mapper 类方法,找到对应的 sql,并封装成 statemnet,下面看看这个 configuration.addMapper(this.mapperInterface) 的实现逻辑吧
MybatisConfiguration.addMapper()
因为是 MybatisPlus,所以源码内部的 Configuration 类是 MybatisConfiguration,查看他的 addMapper() 方法源码
@Override
public <T> void addMapper(Class<T> type) {
mybatisMapperRegistry.addMapper(type);
}再进入 mybatisMapperRegistry.addMapper(type) 源码
@Override
public <T> void addMapper(Class<T> type) {
if (type.isInterface()) {
if (hasMapper(type)) {
// TODO 如果之前注入 直接返回
return;
}
boolean loadCompleted = false;
try {
// TODO 注册mapper类对应的代理工厂类,用于生成代理对象
knownMappers.put(type, new MybatisMapperProxyFactory<>(type));
MybatisMapperAnnotationBuilder parser = new MybatisMapperAnnotationBuilder(config, type);
// 解析mapper类,生成 statement
parser.parse();
loadCompleted = true;
} finally {
if (!loadCompleted) {
knownMappers.remove(type);
}
}
}
}进入 parse() 方法查看
@Override
public void parse() {
String resource = type.toString();
if (!configuration.isResourceLoaded(resource)) {
// 解析mapper.xml
loadXmlResource();
configuration.addLoadedResource(resource);
String mapperName = type.getName();
assistant.setCurrentNamespace(mapperName);
// 解析缓存
parseCache();
parseCacheRef();
IgnoreStrategy ignoreStrategy = InterceptorIgnoreHelper.initSqlParserInfoCache(type);
for (Method method : type.getMethods()) {
if (!canHaveStatement(method)) {
continue;
}
if (getAnnotationWrapper(method, false, Select.class, SelectProvider.class).isPresent()
&& method.getAnnotation(ResultMap.class) == null) {
parseResultMap(method);
}
try {
// TODO 加入 注解过滤缓存
InterceptorIgnoreHelper.initSqlParserInfoCache(ignoreStrategy, mapperName, method);
parseStatement(method);
} catch (IncompleteElementException e) {
// TODO 使用 MybatisMethodResolver 而不是 MethodResolver
configuration.addIncompleteMethod(new MybatisMethodResolver(this, method));
}
}
// TODO 注入 CURD 动态 SQL , 放在在最后, because 可能会有人会用注解重写sql
try {
// https://github.com/baomidou/mybatis-plus/issues/3038
if (GlobalConfigUtils.isSupperMapperChildren(configuration, type)) {
parserInjector();
}
} catch (IncompleteElementException e) {
configuration.addIncompleteMethod(new InjectorResolver(this));
}
}
parsePendingMethods();
}关注最后注释,注入 CRUD 动态 SQL,其实就是给 BaseMapper 里的方法创建对应的 Statement,查看内部逻辑:
void parserInjector() {
// DefaultSqlInjector.inspectInject();
GlobalConfigUtils.getSqlInjector(configuration).inspectInject(assistant, type);
}这里先获取到默认的 Sql 注入器 DefaultSqlInjector,再调用其 inspectInject() 方法注入 sql
@Override
public void inspectInject(MapperBuilderAssistant builderAssistant, Class<?> mapperClass) {
Class<?> modelClass = ReflectionKit.getSuperClassGenericType(mapperClass, Mapper.class, 0);
if (modelClass != null) {
String className = mapperClass.toString();
Set<String> mapperRegistryCache = GlobalConfigUtils.getMapperRegistryCache(builderAssistant.getConfiguration());
if (!mapperRegistryCache.contains(className)) {
// 根据实体类,根据注解解析出表的信息
TableInfo tableInfo = TableInfoHelper.initTableInfo(builderAssistant, modelClass);
// 拿到所有的AbstractMethod实现类
List<AbstractMethod> methodList = this.getMethodList(mapperClass, tableInfo);
if (CollectionUtils.isNotEmpty(methodList)) {
// 循环注入自定义方法
methodList.forEach(m -> m.inject(builderAssistant, mapperClass, modelClass, tableInfo));
} else {
logger.debug(mapperClass.toString() + ", No effective injection method was found.");
}
mapperRegistryCache.add(className);
}
}
}这里面的 AbstractMethod 的实现类有很多,如下
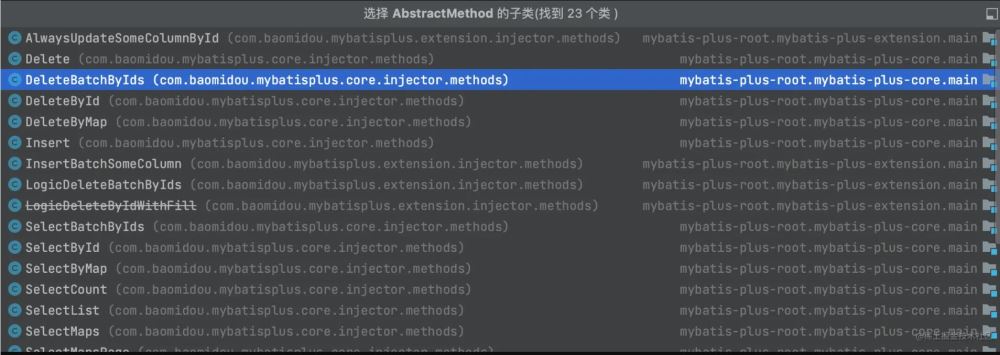
可以说,BaseMapper 中每个方法都有一个对应的 AbstractMethod 实现类,以 selectList() 为例,可以找到 SelectList 类
在下面循环注入的地方:methodList.forEach(m -> m.inject(builderAssistant, mapperClass, modelClass, tableInfo)), 进入 AbstractMethod.inject() 方法
public void inject(MapperBuilderAssistant builderAssistant, Class<?> mapperClass, Class<?> modelClass, TableInfo tableInfo) {
this.configuration = builderAssistant.getConfiguration();
this.builderAssistant = builderAssistant;
this.languageDriver = configuration.getDefaultScriptingLanguageInstance();
/* 注入自定义方法 */
injectMappedStatement(mapperClass, modelClass, tableInfo);
}子类实现了 injectMappedStatement 方法,还是以 SelectList 为例
@Override
public MappedStatement injectMappedStatement(Class<?> mapperClass, Class<?> modelClass, TableInfo tableInfo) {
// selectList sql 模版
SqlMethod sqlMethod = SqlMethod.SELECT_LIST;
// 格式化sql
String sql = String.format(sqlMethod.getSql(), sqlFirst(), sqlSelectColumns(tableInfo, true), tableInfo.getTableName(),
sqlWhereEntityWrapper(true, tableInfo), sqlOrderBy(tableInfo), sqlComment());
// 封装成 sqlSource
SqlSource sqlSource = languageDriver.createSqlSource(configuration, sql, modelClass);
// 注册 mapperStatement
return this.addSelectMappedStatementForTable(mapperClass, methodName, sqlSource, tableInfo);
}其中 sqlSelectColumns(tableInfo, true) 方法是构造出 select 的所有列名,并加上动态sql标签
<choose>
<when test="ew != null and ew.sqlSelect != null">
${ew.sqlSelect}
</when>
<otherwise>id,name,age,email</otherwise>
</choose>其中 sqlWhereEntityWrapper(true, tableInfo) 方法是构造出 where 后面的条件语句,并加上动态sql标签
<if test="ew != null">
<where>
<if test="ew.entity != null">
<if test="ew.entity.id != null">id=#{ew.entity.id}</if>
<if test="ew.entity['name'] != null"> AND name=#{ew.entity.name}</if>
<if test="ew.entity['age'] != null"> AND age=#{ew.entity.age}</if>
<if test="ew.entity['email'] != null"> AND email=#{ew.entity.email}</if>
</if>
<if test="ew.sqlSegment != null and ew.sqlSegment != '' and ew.nonEmptyOfWhere">
<if test="ew.nonEmptyOfEntity and ew.nonEmptyOfNormal"> AND</if> ${ew.sqlSegment}
</if>
</where>
<if test="ew.sqlSegment != null and ew.sqlSegment != '' and ew.emptyOfWhere">
${ew.sqlSegment}
</if>
</if>最后 format 后的 sql 语句是
<script>
<if test="ew != null and ew.sqlFirst != null">
${ew.sqlFirst}
</if> SELECT <choose>
<when test="ew != null and ew.sqlSelect != null">
${ew.sqlSelect}
</when>
<otherwise>id,name,age,email</otherwise>
</choose> FROM demo_user
<if test="ew != null">
<where>
<if test="ew.entity != null">
<if test="ew.entity.id != null">id=#{ew.entity.id}</if>
<if test="ew.entity['name'] != null"> AND name=#{ew.entity.name}</if>
<if test="ew.entity['age'] != null"> AND age=#{ew.entity.age}</if>
<if test="ew.entity['email'] != null"> AND email=#{ew.entity.email}</if>
</if>
<if test="ew.sqlSegment != null and ew.sqlSegment != '' and ew.nonEmptyOfWhere">
<if test="ew.nonEmptyOfEntity and ew.nonEmptyOfNormal"> AND</if> ${ew.sqlSegment}
</if>
</where>
<if test="ew.sqlSegment != null and ew.sqlSegment != '' and ew.emptyOfWhere">
${ew.sqlSegment}
</if>
</if> <if test="ew != null and ew.sqlComment != null">
${ew.sqlComment}
</if>
</script>最后是把 sql 封装成了 SqlSource,并构造 MapperStatement 存入 configuration.mappedStatements 中,后面 mapper 调用 selectList 方法时,会从 mappedStatements 中找到对应的 statement,并取出 sql 语句执行,就能拿到数据了
小结
到此,MybatisPlus BaseMapper 实现对数据库增删改查源码解析完毕,相信通过源码的阅读能对 mybatisPlus 有更深的了解
到此这篇关于MybatisPlus BaseMapper 实现对数据库增删改查源码解析的文章就介绍到这了,更多相关MybatisPlus BaseMapper 数据库增删改查内容请搜索码农之家以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章希望大家以后多多支持码农之家!